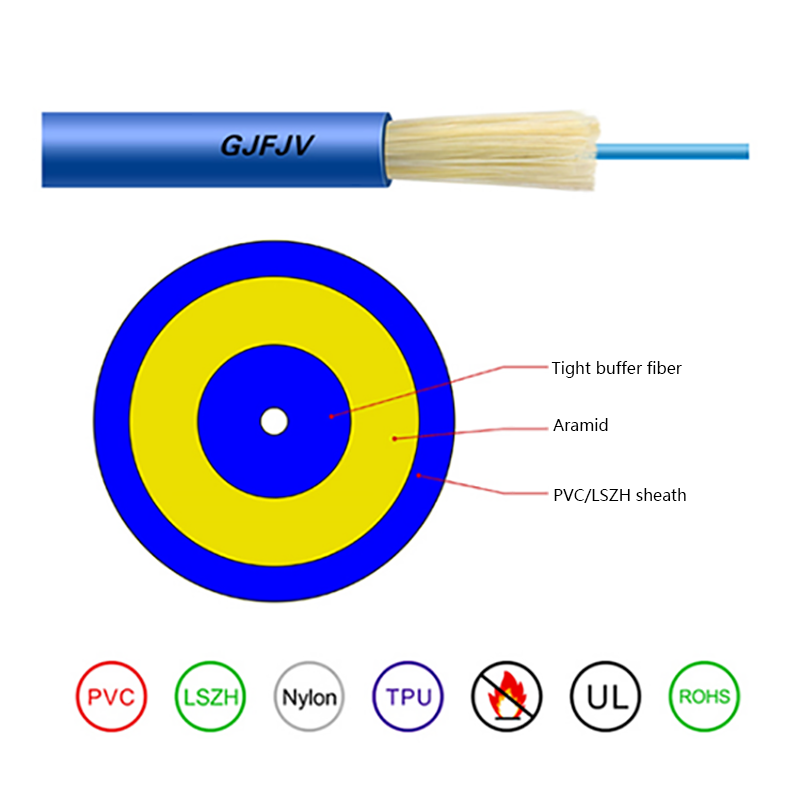
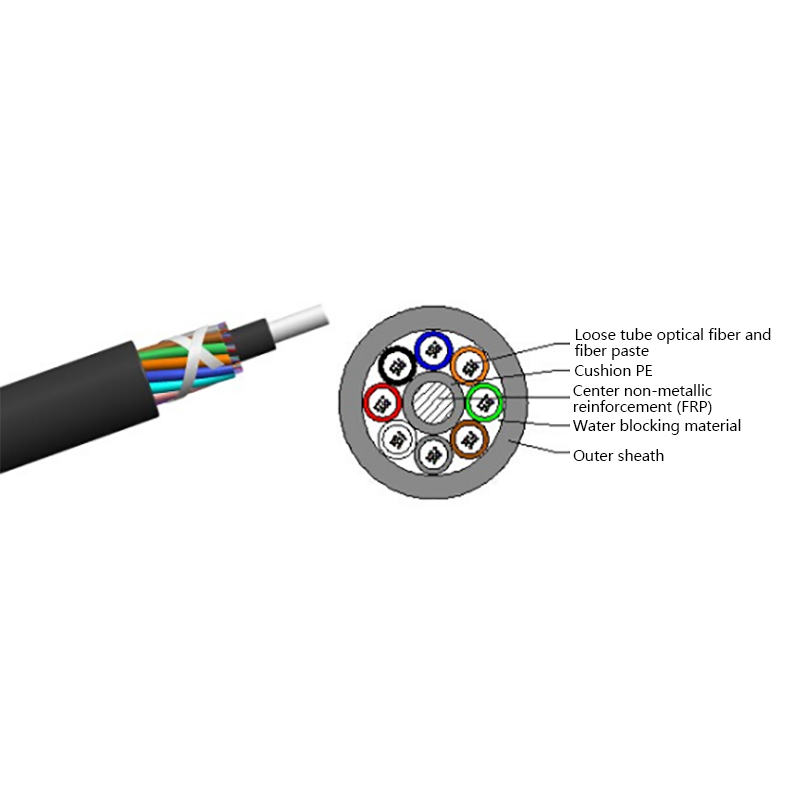
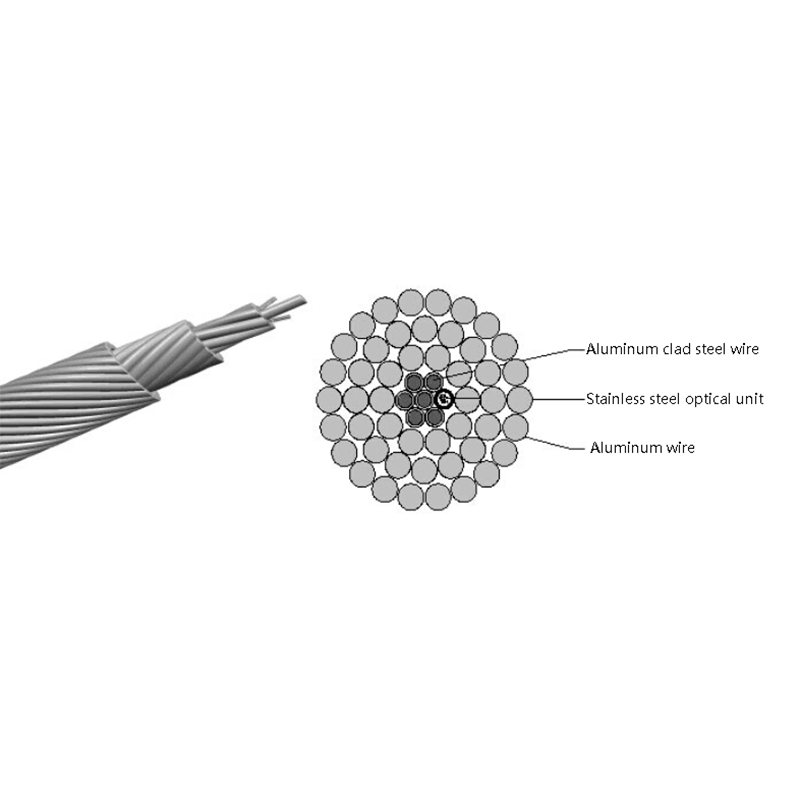
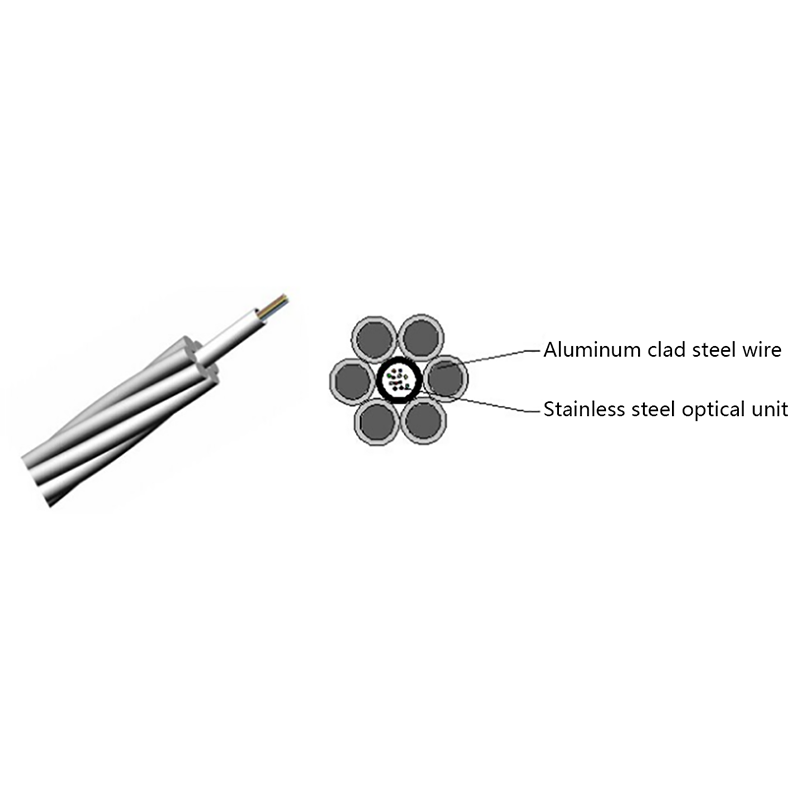
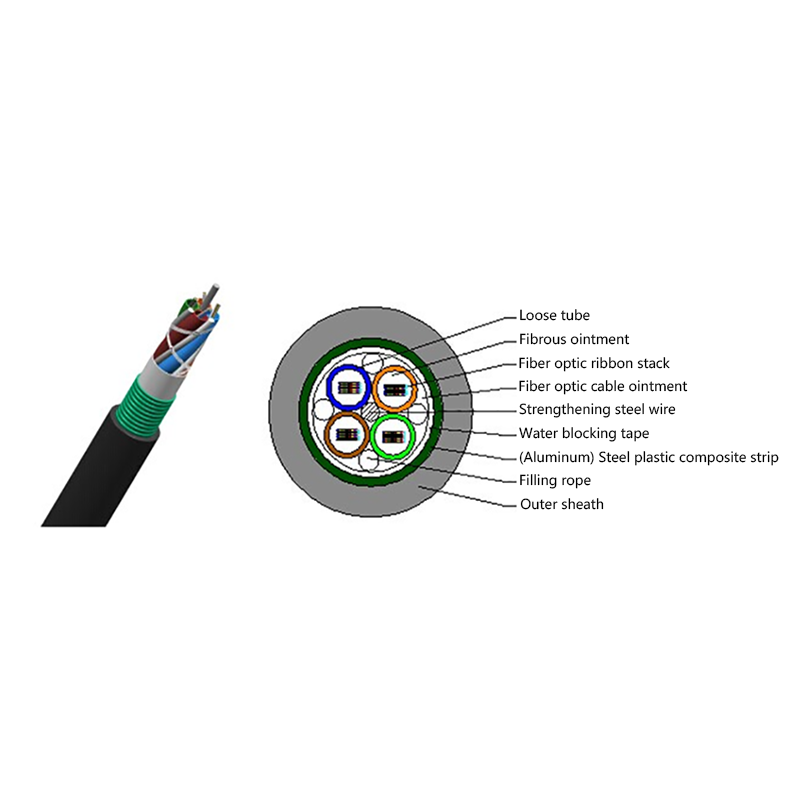
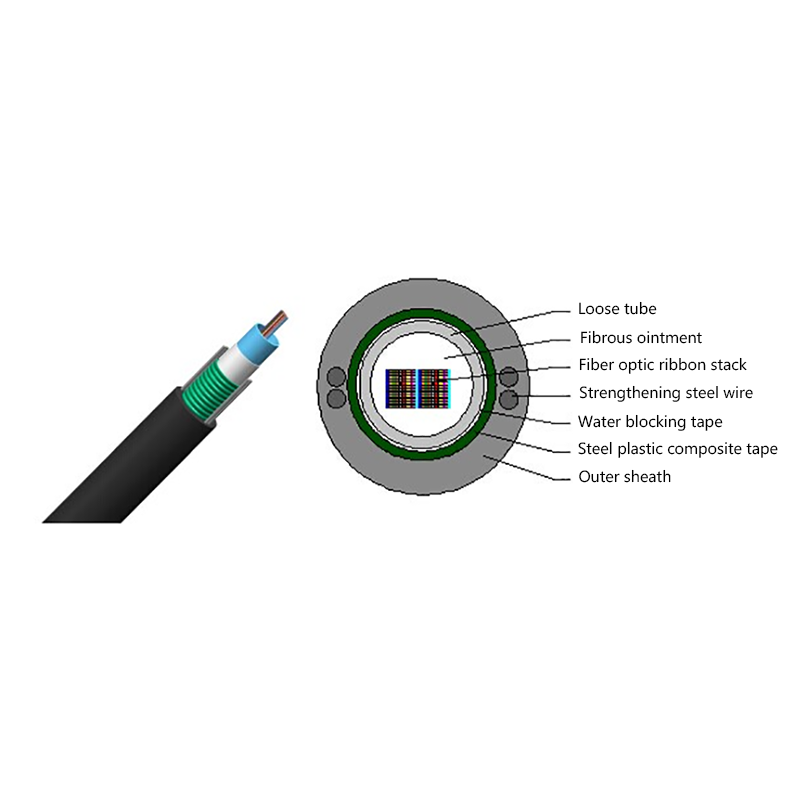
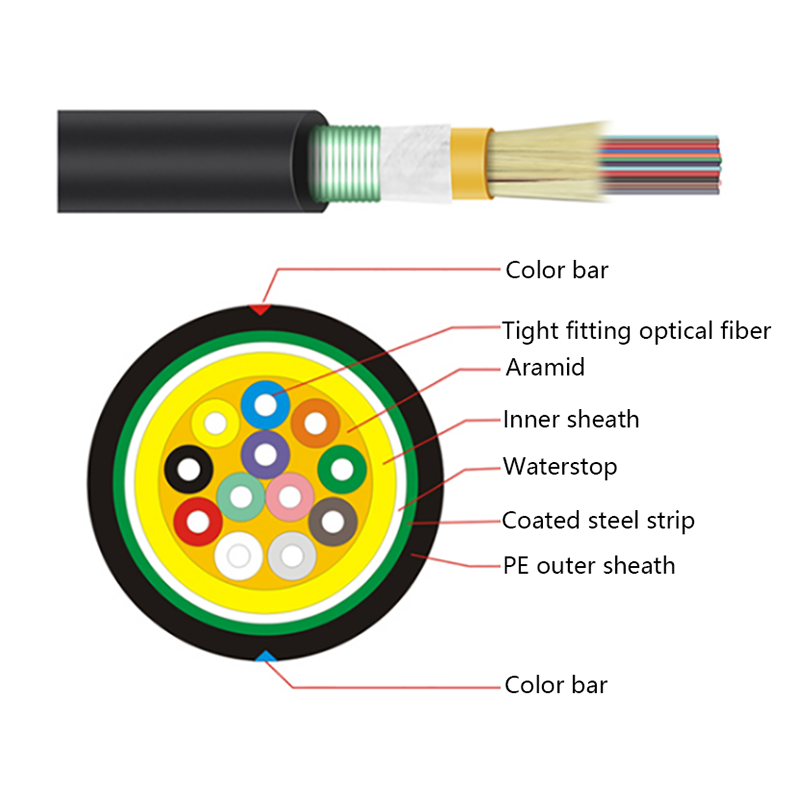
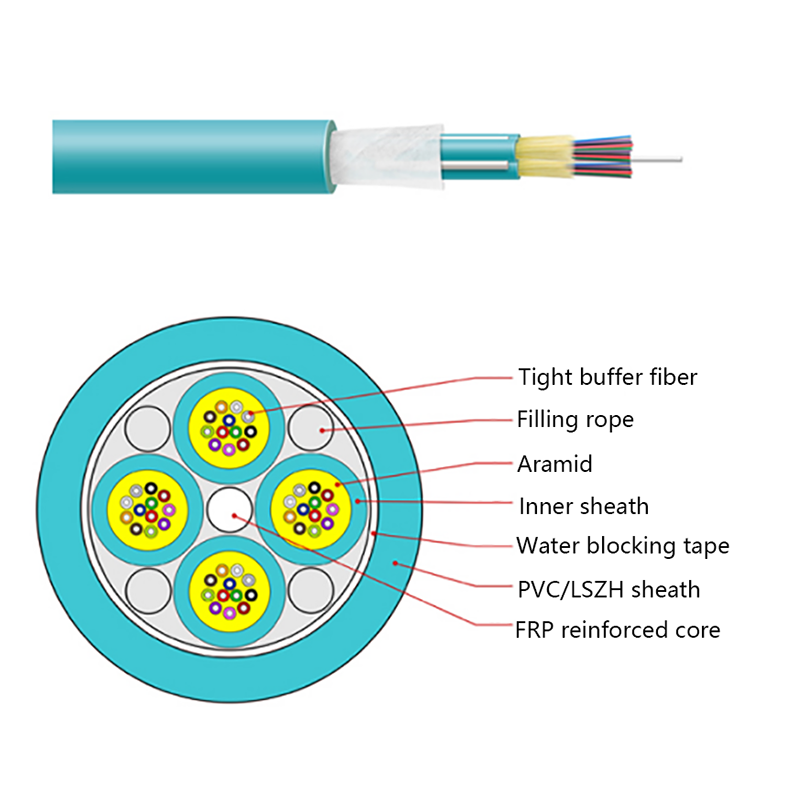
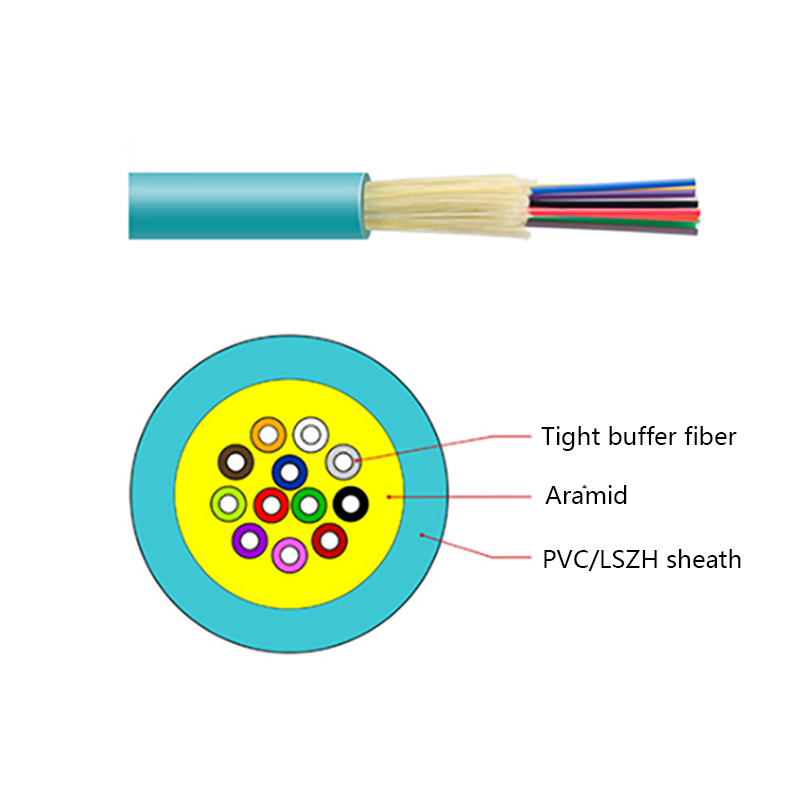
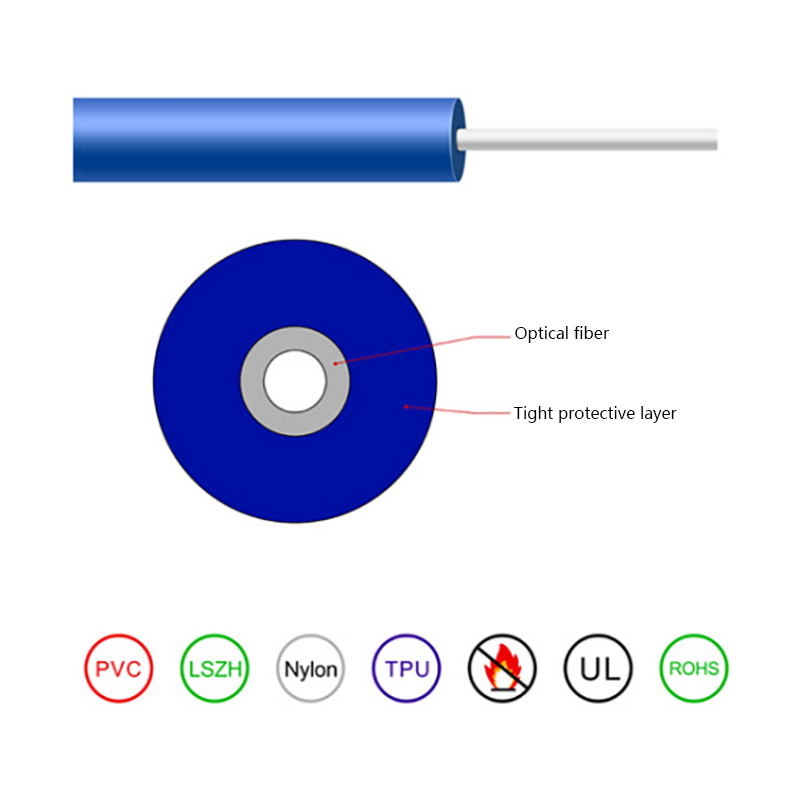
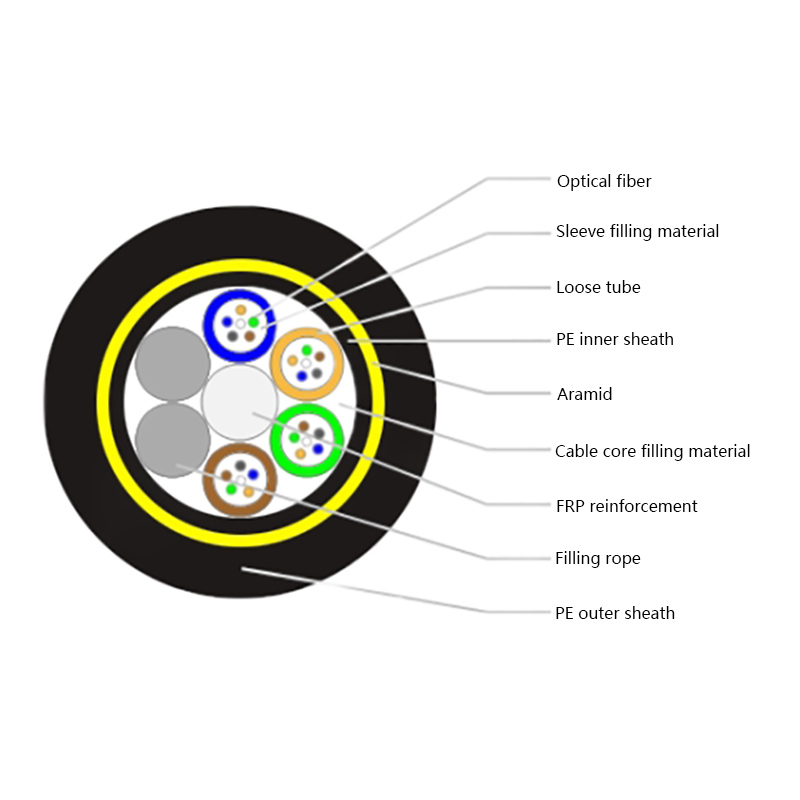
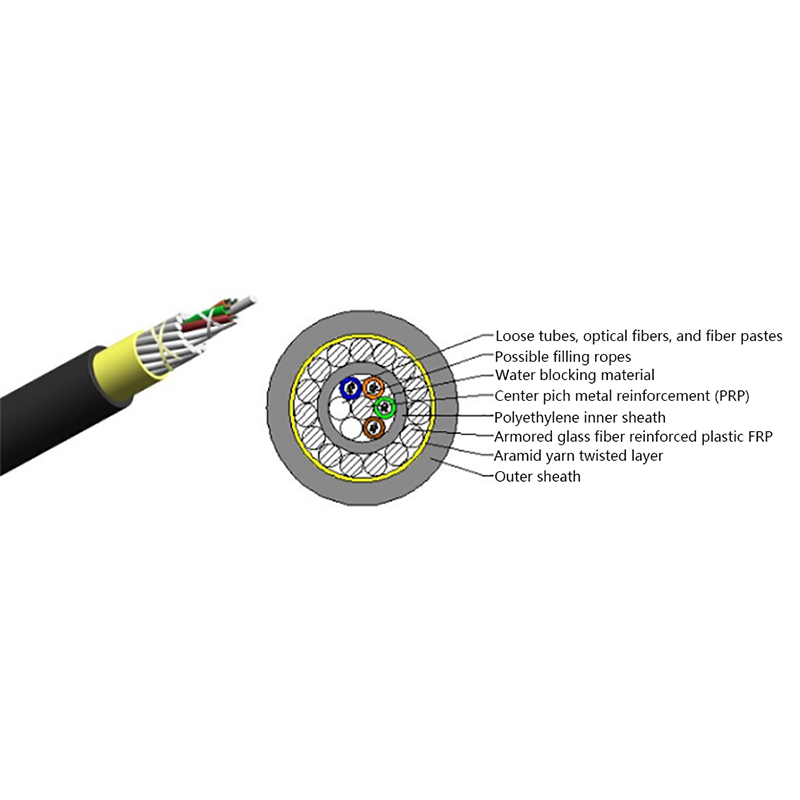
How is the performance of indoor optical cables affected by environmental conditions such as temperature or humidity?
Indoor optical cables are essential components of modern communication infrastructure, offering high-speed data transmission with minimal signal degradation. However, the performance of these cables is not impervious to external factors. Environmental conditions, particularly temperature and humidity, can significantly influence the efficiency and longevity of optical fiber systems. Understanding how these factors affect cable performance is critical for ensuring optimal network reliability and durability.
Temperature and Optical Fiber Behavior
Temperature fluctuations are one of the most significant environmental factors impacting indoor optical cables. Optical fibers are made from materials such as glass or plastic, which expand and contract with temperature changes. Extreme temperature variations can lead to physical stress, potentially causing the fiber to bend or even break under strain. This can result in signal attenuation, where the light signal loses strength over distance, leading to a reduction in transmission quality.
High temperatures can also accelerate the aging process of the cable's protective coatings. The polymer materials that encase the fiber can degrade over time, weakening their protective function. As the protective layer breaks down, the fiber becomes more susceptible to physical damage, such as abrasion or exposure to environmental pollutants. Consequently, optical cables subjected to prolonged high temperatures may experience a significant reduction in service life.
On the other hand, low temperatures can cause optical fibers to become brittle, making them more prone to cracking or snapping under mechanical stress. While this effect is less pronounced than the degradation caused by high heat, the fragility of fibers at low temperatures still poses a risk, especially in regions with extreme winter conditions.
Humidity and Its Effects on Fiber Optic Cables
Humidity is another environmental condition that can influence the performance of indoor optical cables. Optical fibers are generally resistant to water; however, prolonged exposure to high humidity levels can impact the cable’s outer materials. Moisture can seep into the cable’s protective sheathing, leading to the growth of mold, corrosion of metallic components, or swelling of the cable's insulative layers. Over time, this degradation can compromise the structural integrity of the cable.
One of the most critical issues arising from high humidity is the potential for water-induced attenuation. When moisture infiltrates the optical fiber, it may lead to signal distortion as the water can interact with the light signals passing through the fiber. This can result in increased loss of signal strength, effectively reducing the overall efficiency of data transmission.
Furthermore, excessive humidity can cause swelling or softening of the cable’s sheathing material, leading to mechanical weakness. In turn, this may result in the cable losing its shape or becoming more vulnerable to physical damage, particularly during installation or routine maintenance.

Synergistic Effects of Temperature and Humidity
While both temperature and humidity individually affect indoor optical cables, their combined influence can be even more detrimental. High temperatures paired with high humidity levels can exacerbate material degradation, accelerating the deterioration of protective coatings and insulation. This synergistic effect increases the likelihood of physical damage, performance degradation, and ultimately, a shortened service life.
Similarly, a sudden transition from a warm environment to a cold one, coupled with high humidity, can cause condensation within the cable. This moisture can lead to internal short circuits or signal attenuation, particularly in cables with inadequate sealing or waterproofing.
Mitigating Environmental Impact
To ensure the optimal performance of indoor optical cables, manufacturers incorporate protective features such as moisture-resistant coatings, temperature-stable polymers, and carefully designed sheathing materials. Choosing the right cable for specific environmental conditions is essential. For instance, cables designed for environments with high humidity levels often feature reinforced water-blocking layers, while those exposed to significant temperature extremes may include materials that can withstand expansive thermal changes.
Proper installation also plays a crucial role in mitigating environmental risks. Cables should be placed in areas where temperature and humidity fluctuations are minimal, avoiding areas exposed to direct sunlight, moisture accumulation, or excessive heat. Additionally, cable management systems, including climate-controlled enclosures, can provide an extra layer of protection.
The performance of indoor optical cables is undeniably affected by environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity. Temperature extremes can cause physical stress on the fiber and degrade protective coatings, while excessive humidity can lead to material deterioration and signal attenuation. Understanding these effects and taking preventative measures through the selection of appropriate materials and careful installation practices is crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliability of optical fiber networks. By addressing these environmental challenges, businesses can maximize the efficiency and durability of their optical cable systems, ensuring seamless communication infrastructure for years to come.



 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体